best office chair for back posture

How to Adjust Office Chairs What is the most important part about having a good workstation? The office workstation should let the worker sit and carry out their duties in comfort while allowing for voluntary changes in the working position. There are three contact areas in the work space that affect the worker's posture: the seat, the work surface (commonly it is a desk top or keyboard) and the floor. To ensure the most comfortable posture possible, two of these factors have to be adjustable. If you can afford to do nothing else, a fully adjustable chair is a "must". The other, and perhaps the most preferable option, would be a fully adjustable desk. However the price of such a desk may not make this option practical. Another effective (and cheaper) option is to use an adjustable chair and footrest to secure postural comfort. What should I consider when selecting a chair? A basic rule of ergonomics is that there is no such thing as an "average" person. However, providing a chair specifically designed for each individual is not practical.

The only solution is to provide workers with fully adjustable chairs that can accommodate a maximum range of people (typically around 90 percent of the population; workers falling in the ranges of 5% of the shortest and the tallest will need custom-made chairs). Choose a chair with: Controls that are easy to operate from sitting position.
chair for sale in bangalore A seat that adjusts for both height and tilt.
ikea office chair repair A seat that does not put pressure the back of thighs or knees.
harveys furniture store table and chairs A seat with a front edge that curves towards the floor.
chaise lounge chair patterns
Breathable, non-slippery fabric on the seat. A backrest shaped to support the lower back. A stable five-point base. Wheels or casters suitable for the type of flooring. Armrests that can be adjusted to the elbow height when your upper arms are hanging down and your forearms are at about a 90 degree angle to the upper arms.
where to buy anti gravity chair Armrests that do not interfere with free movements within the workstation.
white chair covers birmingham You may also wish to check the OSH Answers document The Ergonomic Chair for more details on how to purchase a chair. What is so controversial about armrests? Armrests were traditionally not recommended because they can prevent the users from getting close enough to the desk. However, armrests that extend 25 cm (10 inches), or less, from the back of seat may be appropriate.
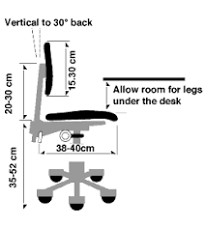
People using chairs fitted with these shorter armrests can move their chairs closer to their workstations. The armrests gives them a place to rest their arms which, in turn, takes some of the load off their shoulders and neck. How do I adjust a chair for my height? Stand in front of the chair. Adjust the height so the highest point of the seat, (when in the horizontal position), is just below the knee cap. Sit on the chair and keep your feet flat on the floor. Check that the clearance between the front edge of the seat and the lower part of the legs (your calves) fits a clenched fist (about 5 cm or 2 inches). Adjust the back rest forwards and backwards as well as up and down so that it fits the hollow in your lower back. Sit upright with your arms hanging loosely by your sides. Bend your elbows at about a right angle (90 degrees) and adjust the armrest(s) height until they barely touch the undersides of the elbows. Remove the armrests from the chair if this level can not be achieved or if armrests, in their lowest adjustment, elevate your elbows even slightly.

Tilt the seat itself forwards or backwards if you prefer. Different office tasks require different equipment, accessories and layouts. Nonetheless, the chair and its adjustment remain constant for the majority of setups in a typical office environment. What adjustments should I make if the workstation (desk) is at a fixed height? Once your chair is properly adjusted for your height, check if you can sit at the workstation comfortably with your legs underneath. If you cannot fit your legs under the workstation or there is not enough space to move them freely, your workstation is too low for you and you should not use such a workstation on a regular basis! If you can sit comfortably but need to elevate your arms in order to place them over the work surface, your workstation is too high. Adjust the chair height so your elbows are about the same height as the work surface. Use a footrest if you cannot place your feet flat on the floor. The footrest should be adjustable and support both feet.

Keep feet flat and firm on the footrest. Although every effort is made to ensure the accuracy, currency and completeness of the information, CCOHS does not guarantee, warrant, represent or undertake that the information provided is correct, accurate or current. CCOHS is not liable for any loss, claim, or demand arising directly or indirectly from any use or reliance upon the information.Comprehensive Buying Guides and Tips For Office Comfort!The wrong chair = real health problems. (Total read time: 8 minutes) In this post I’ll cover how I identified the best high-end chairs in the world, which I ultimately chose, and the tangible results that followed. In January of 2005, I found myself on a veranda in Panama after the usual afternoon rain, dreaming of the upcoming year and reflecting on lessons learned since leaving the US. Maria Elena, the matriarch of the Panamanian family that had adopted me, sipped her iced tea and pointed at my bruised feet: “Tim, let me share some advice I was once given.

Buy the most comfortable bed and pair of shoes you can afford. If you’re not in one, you’ll be in the other.” I followed her advice upon returning to CA and the results were sudden: Plantar Fasciitis disappeared, as did shoulder impingement after switching from coil-spring to foam-layered mattresses. But what about chairs? On January 4th, 2009, I tweeted out the following: “Is the Aeron chair worth it? http://tr.im/2uxd Do you have any fave chairs for extended sitting and writing?” Even though I’m financially comfortable now, I didn’t grow up spending a lot of money, which I’m thankful for. To this day, I’ve never paid for first-class airfare for myself. Not that it isn’t worth it — I just can’t do it. Similarly, I had trouble believing a chair could possibly be worth $850-$1,200, but my back pain led me to pose the question to the omniscient Interweb. More than 95% of Aeron users replied with “yes, absolutely”, but it wasn’t the only chair with a cult-like following.

Four of the five are manufactured by Herman Miller (HM) and Humanscale (HS). Prices are from Amazon, as are the star reviews, but discounts of $200-400 can be negotiated with dealers. Both eBay and Craiglist offer similar discounts. In descending order of popularity: 1. Aeron (Fully loaded) (HM) – $879 (1 review; average review: 5 stars) Used at NASA mission control and tech start-ups worldwide. 2. Mirra (fully loaded) (HM) – $829 (14 reviews; average review: 4.5 stars) Note: the Herman Miller sales representatives I spoke with preferred the Mirra seat feel for shorter legs vs. the Aeron. Easier to adjust: Mirra is about 9 revolutions from loosest to tightest settings; 3. SwingChair – $495 Recommended by a strong contingent of writers, including one of my favorite visual storytellers, Kathy Sierra. I like the design concept, but I would suggest other forms of “core exercise”. 4. Liberty (HS) – $899 (6 reviews; average review: 3.5 stars) 5. Freedom Task Chair with Headrest (HS) – $999.99 (1 review, average: 4 stars) Used at the FBI and by other governmental agencies with three-letter acronyms.

6. Embody – $1,800 list price (negotiated with dealer: $1,200-1,300): Basis of chair design – sitting is bad; Even in locked position, it still has some backward flex at the top position. No forward tilt option. For personal testing, I also added a Swiss-ball chair (Isokinetics Balance Ball Chair – $75) to the mix, as seen below: Surprisingly, the Isokinetics chair is more comfortable than most fixed chairs I tested, though there is some minor… ahem… testicular compression that isn’t nearly as pleasant as it sounds. If you don’t have jewels to worry about, this chair could well be an ideal cost-effective choice. The chair I most wanted to test was the Mirra, which seems to have the best combination of price point (bought used or via eBay) and multiple 5-star reviews. Not to mention it’s also the name of one of the best BMXers of all time. In the end, I bought a used C-size (technically a bit too large for me) Aeron for $450 on Craigslist. I’m impatient and didn’t want to wait over the weekend to schedule sittings for other Herman Miller chairs with a certified dealer.

Once I have some conclusive comparable data, I want closure.I’m 5′ 8″ and 170 lbs., but the C works with no problem. 1) The lumbar support is — by far — the primary determinant of comfort or pain. I’ve lowered this adjustment and found that maintaining the natural S-curve through pressure on the lower back is what prevents pain most consistently. Comfortable sitting time is now 7-8 hours vs. less than 2 hours, with no ill after-effects. Sliding lumbar support on the Aeron. 2) Seat height (and secondarily, depth) will determine the rest. If the flats of your feet don’t make complete contact with the floor, you will move your hips forward and slouch, eliminating the S-curve in the lower lumbar. If your seat is too low and your knees are above your hips, you will shorten the habitual range your hip flexors (negative neural adaptation) and end up with severe lower-back pain. Aim to keep your hamstrings parallel to the floor, and if the seat is too long for your femur (thigh bone) — as is mildly the case with my C-size Aeron — just separate your knees a bit.

If you’re not wearing a tight skirt, I’ve found a basketball of space between the knees to provide the best lateral stabilization, which reduces torso fatigue. Take off heels when sitting at a desk, lest you end up with hot calves and Quasimodo-like posture. Not good for mating. If you are wearing a tight skirt, I suggest taking up the Japanese tea ceremony and sitting on tatami side saddle. It’ll be more comfortable than crossing your legs all day.True, I’ve thought more about chairs in the last few weeks than anyone should, but I do it to save you the trouble. Benefit from my OCD so you can obsess on other things. 3) Using a 3′ long and 6″ diameter foam roller three times per day for 5 minutes can eliminate persistent middle-back pain from mediocre chair use; conversely, it can extend your comfortable sitting time by 30-40%. Knowledge workers often log more ass-in-seat time than sleep. Coders, in particular, are often subjected to a steady diet of Mountain Dew and hunching for 12+-hour marathons.

I don’t put in these hours, but I found myself with severe mid-upper back pain from using a non-adjustable chair and craning over a desk that was too low, even for 30-60 minutes per day. Two doctors suggested various therapies, but a quick experiment (placing a laptop on top of a dresser and writing while standing for two days) proved that posture was the problem. In less than a week following my switch to the Aeron, all upper middle-back (lower trapezius, rhomboid major) pain disappeared completely. The results: better output during work and writing, faster and deeper sleep, and a huge smack on the forehead. Why the hell didn’t I do this earlier? In my case, was it worth it at $450? Particularly looking at the value of time per hour and the lost income due to doctor visits, massage, etc., this is $450 I should have invested years ago. Odds and Ends: Twitter Giveaway WinnersThe travel bag and Fujitsu color travel scanner are gone. More giveaways coming here this week…